Published
- 15 min read
How to Deploy a Laravel App in 2025 (The Simple, Fast and Stress-Free Way)

Deploying a Laravel application can feel more complicated than it needs to be. You configure PHP and its extensions, tune Nginx or Apache, manage .env variables securely, set up queue workers for background jobs, handle caching and session drivers, configure storage disks, and schedule cron tasks.
Every environment behaves slightly differently, so deployments often become slow, repetitive, and error prone.
Most teams keep rebuilding this setup for each project, even though the core deployment steps rarely change.
A smoother approach is to use a platform that automates the repetitive infrastructure work.
Kuberns makes Laravel deployment straightforward by taking your application from GitHub to a production environment with only a few clicks.
It automatically detects the Laravel runtime, installs Composer dependencies, applies production optimizations, configures SSL, manages scaling, and provides live logs and performance monitoring. This creates a consistent deployment workflow across development, staging, and production environments.
If you are new to the platform, you can read how it works in detail in What is Kuberns, the simplest way to build, deploy, and scale full stack apps.
In this guide, we will cover:
- What you need before deploying Laravel
- How Laravel behaves differently in production
- The fastest way to deploy Laravel on Kuberns
- How to configure environment variables, queue workers, storage, and SSL
- Common deployment issues and how to avoid them
This is written for developers and teams who want a clean, repeatable deployment workflow without complex DevOps steps or server maintenance.
Understanding How Laravel Runs in Production
Laravel needs a consistent and well-configured environment to run smoothly in production. It is not just about running PHP, but making sure background jobs, scheduling, and environment variables work together reliably.
A stable Laravel production setup usually includes:
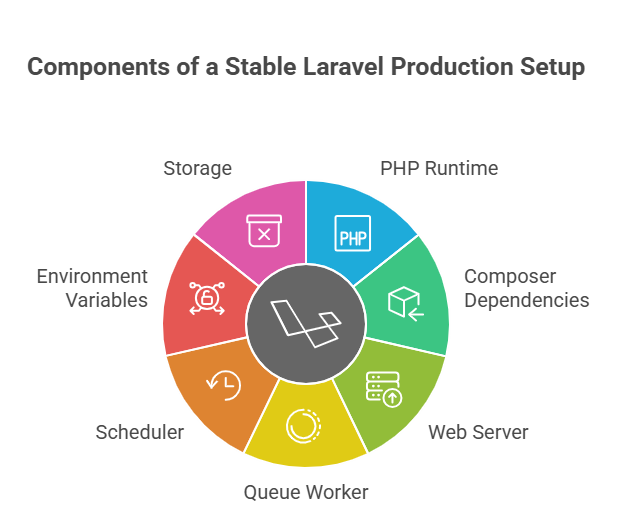
- PHP runtime (8.1 or newer) running with PHP-FPM
- Composer dependencies installed in production mode
- A web server routing requests to the public folder
- A queue worker running continuously
- A scheduler that triggers Laravel’s task runner
- Environment variables stored securely
- Storage that persists logs and uploaded files
When managing this manually, every step above must be installed, configured, secured, and maintained across staging and production environments.
Kuberns automates this setup. When you connect your Laravel repository, it detects the framework, installs dependencies, optimises your build, configures the PHP runtime, and lets you enable queue workers and the scheduler without editing server files. SSL is applied with one click, and the same environment is used across dev, staging, and production.
This approach follows the same deployment consistency described in Deploy Nodejs on Netlify and Why Kuberns is a Smarter Choice, where the environment stays predictable across every deployment.
In short: You focus on your Laravel code. Kuberns takes care of the infrastructure.
Before Deploying Your Laravel App
Before deploying, your Laravel project should be in a clean and production-ready state. This prevents failed builds, missing keys, and unexpected environment issues once the application is live.
Make sure your project has:
- A properly configured .env file in your local environment
- A valid APP_KEY generated using php artisan key:generate
- composer.json located at the project root (not inside a subfolder)
- The public folder acting as the main web entry point
- Database credentials ready to be added to the deployment environment
Queue and Cache Preparation
If your app uses queues or asynchronous tasks:
- Set the queue driver to redis or database
- Confirm Redis or your DB is accessible in your production environment
- Note your worker command so you can enable it later (on Kuberns, you’ll simply add it in the worker settings)
Example .env Values (Inline)
APP_ENV=production APP_KEY=your-generated-key APP_DEBUG=false APP_URL=https://yourdomain.com
DB_CONNECTION=pgsql DB_HOST=your-db-host DB_PORT=5432 DB_DATABASE=your-db DB_USERNAME=your-db-user DB_PASSWORD=your-db-password
Quick Verification Checklist
- Run php artisan config:clear locally if you recently updated .env
- Ensure storage and bootstrap/cache directories have write permissions
- Commit and push your latest migrations
This same environment preparation approach is explained in Deploy Nodejs on Netlify and why Kuberns is a smarter choice which highlights how consistent, preconfigured runtime environments help avoid deployment issues.
You can read it here: Deploy Nodejs on Netlify and why Kuberns is a smarter choice
How to Deploy Laravel on Kuberns in Under 2 Minutes
Once your Laravel project is ready, the deployment process on Kuberns is straightforward. The platform automatically handles runtime detection, build steps, scaling, and environment configuration, so you do not need to write a Dockerfile or configure a server manually.
Step 1: Connect Your Repository
 Open the Kuberns dashboard and select Connect GitHub. Choose your Laravel repository and pick the branch you want to deploy. Kuberns pulls the source code directly and tracks updates for future deployments.
Open the Kuberns dashboard and select Connect GitHub. Choose your Laravel repository and pick the branch you want to deploy. Kuberns pulls the source code directly and tracks updates for future deployments.
Step 2: Automatic Laravel Detection
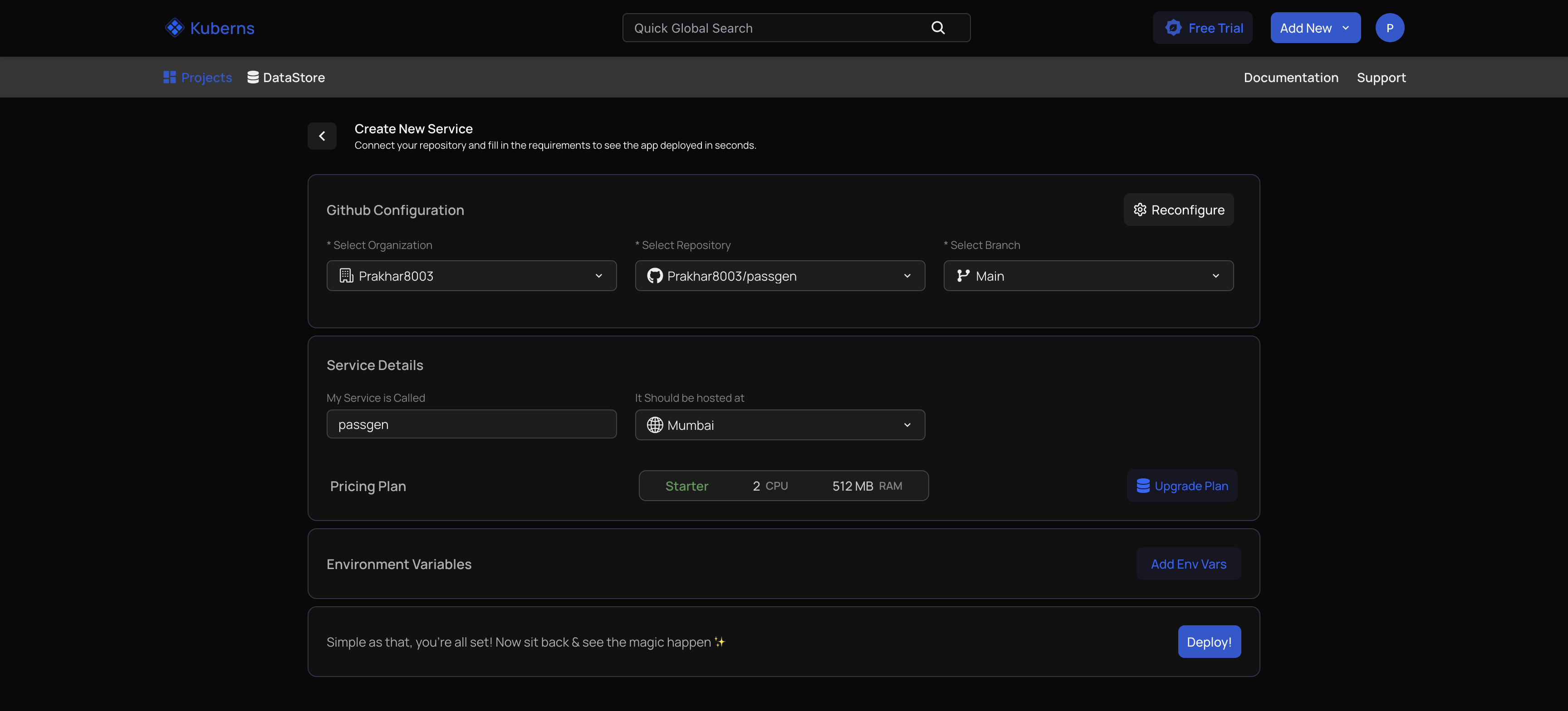 Kuberns analyzes your repository and recognizes that it is a Laravel application. It automatically sets up:
Kuberns analyzes your repository and recognizes that it is a Laravel application. It automatically sets up:
- The correct PHP runtime version
- Composer install during the build stage
- Laravel optimization commands (config, route, view caching)
- A preconfigured web server pointing to the public directory
No manual Nginx setup, no Dockerfile, and no server configuration required.
Step 3: Add Environment Variables
 Open the Environment section in the dashboard and paste your .env values. They are stored securely, encrypted at rest, and injected at runtime. This ensures passwords, API keys, and database credentials are never hardcoded in your codebase.
Open the Environment section in the dashboard and paste your .env values. They are stored securely, encrypted at rest, and injected at runtime. This ensures passwords, API keys, and database credentials are never hardcoded in your codebase.
Step 4: Deploy Your Application
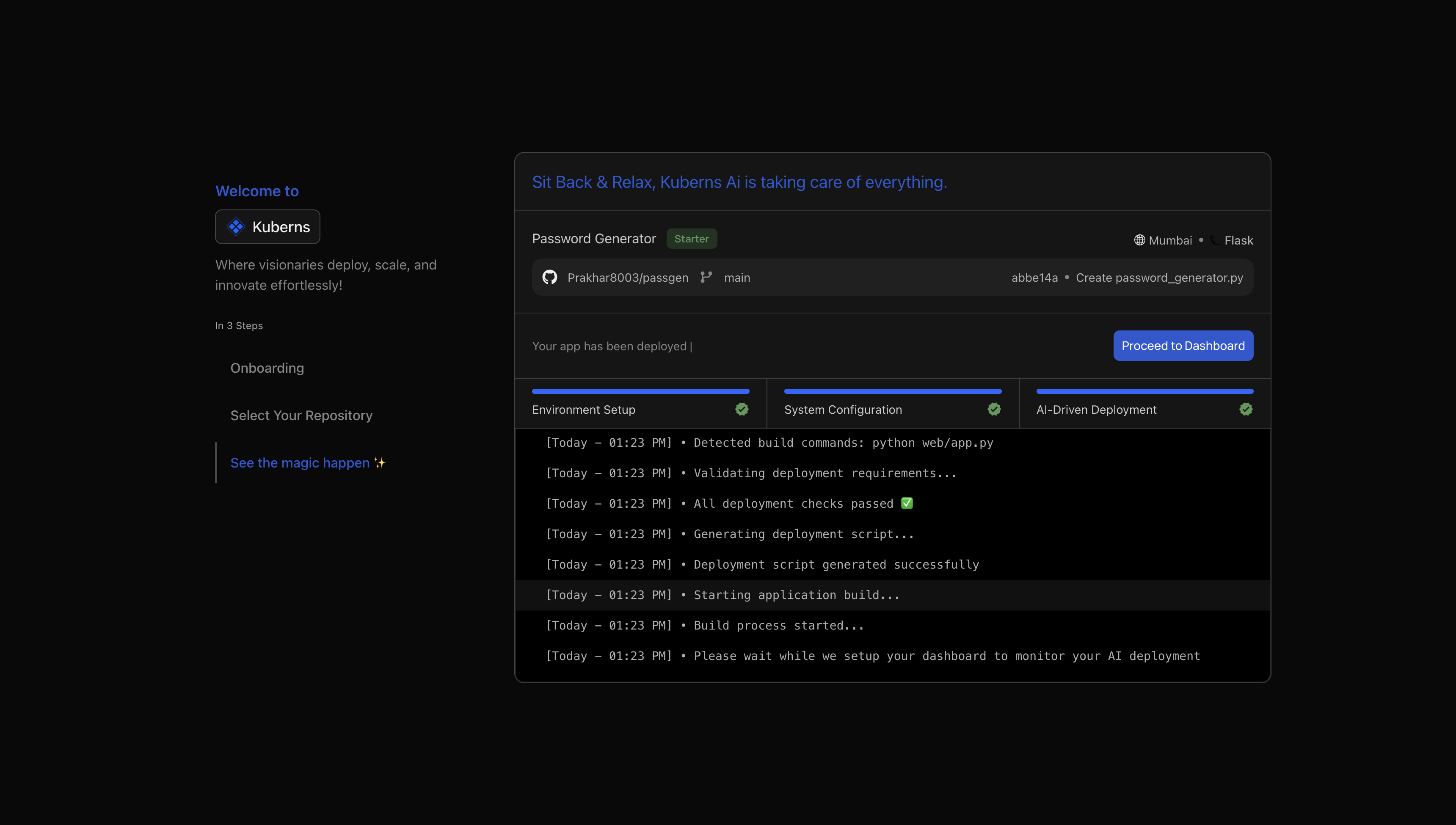 Click Deploy. During the build, you will see steps such as:
Click Deploy. During the build, you will see steps such as:
- Composer dependency installation
- Laravel caching and optimization
- Application packaging and container creation
After the deployment completes, Kuberns assigns a live preview URL so you can open and test your application immediately.
Step 5: Add a Custom Domain (Optional)
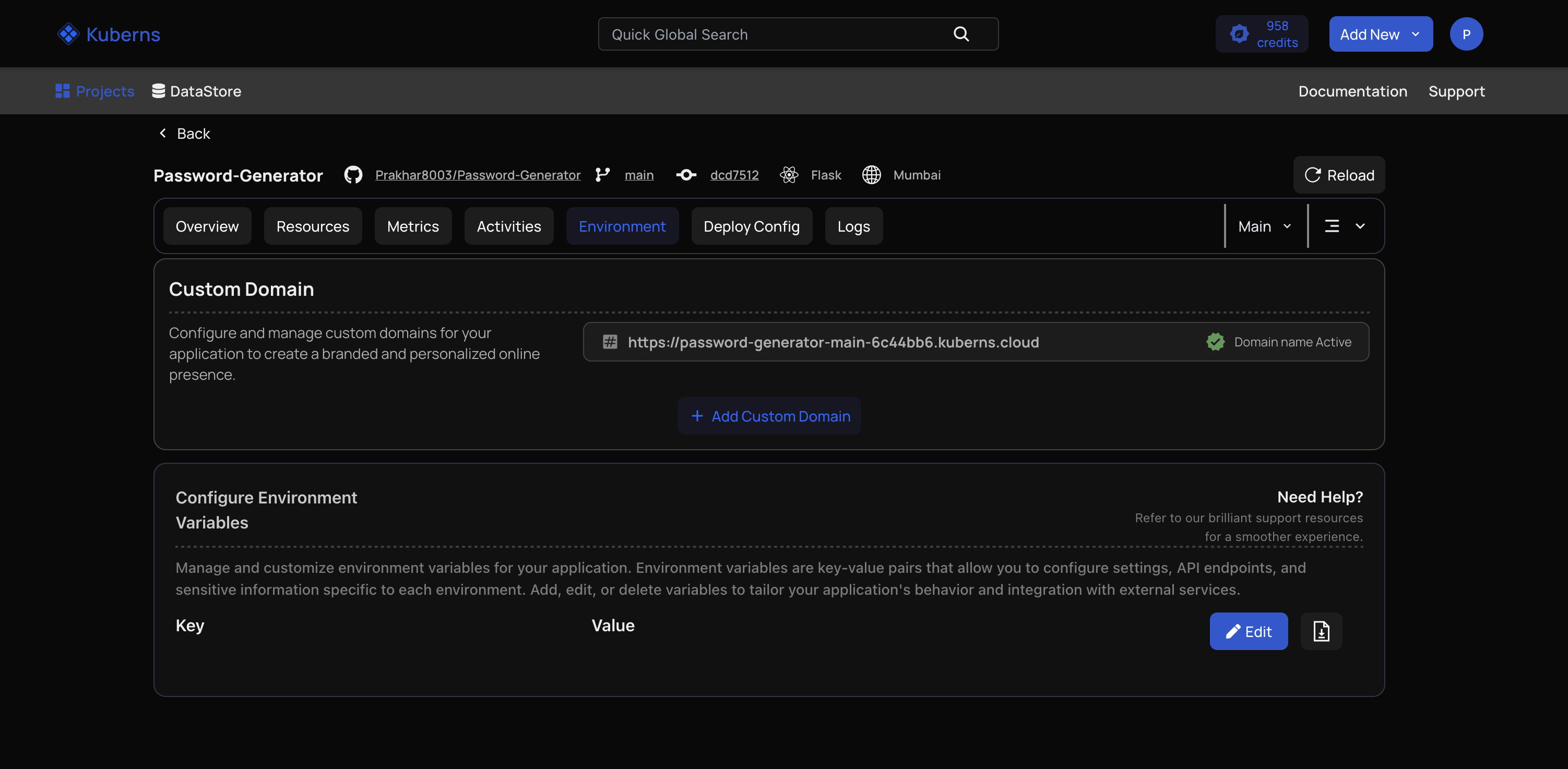 If you want to use your own domain, simply point your DNS CNAME to the address shown in the dashboard. Enable SSL with one click to secure your app with HTTPS automatically.
If you want to use your own domain, simply point your DNS CNAME to the address shown in the dashboard. Enable SSL with one click to secure your app with HTTPS automatically.
This workflow is consistent with how Kuberns handles other frameworks as well.
For example, the process described in Node.js Deployment Tutorial in the Kuberns documentation shows the same simplicity for environment setup and runtime handling.
The core idea stays the same: you focus on the application, the platform handles the infrastructure.
Running Queue Workers on Kuberns
If your Laravel application uses queued jobs (for example, anything triggered with Queue::dispatch()), you need a worker running continuously to process those jobs.
On Kuberns, you do not have to configure Supervisor or manage system services. You simply add a Worker Resource from the dashboard.
Example worker configuration (inline):
Name: worker Command: php artisan queue: work —sleep=3 —tries=3
Kuberns ensures the worker runs continuously, restarts automatically if it stops, and scales it if your application experiences load. If you are using Redis for queues, make sure REDIS_HOST, REDIS_PORT, and authentication variables are added to your environment settings.
This is the same runtime consistency Kuberns applies in its other environments as described in the Node.js Deployment Tutorial in the docs.
Running Laravel Scheduler
Laravel’s scheduler triggers recurring tasks using a single CLI command:
php artisan schedule: run
On a normal VPS, this would require adding a cron entry. On Kuberns, scheduling is built in. Just enable the Scheduler toggle in your service settings and the platform runs the scheduler automatically at the correct interval.
No cron configuration. No system-level access needed. No maintenance required.
Managing File Storage (Uploads, Media, Logs)
Many Laravel applications need persistent storage for user uploads, images, or generated files. The recommended setup is:
- Use S3 or S3 compatible storage
- Store access keys in environment variables
- Set FILESYSTEM_DISK=s3 in .env
Kuberns supports attaching persistent volumes if your app requires local filesystem persistence, but S3 backed storage is ideal for scaling, backups, and performance.
Logs, Monitoring, and Debugging
Kuberns provides real-time logs directly in the dashboard:
- Application web process logs
- Queue worker logs
- Scheduler run logs
You can view, filter, and share logs without accessing a server. Additionally, Kuberns provides request analytics, resource usage graphs, and automatic alerts if the application becomes unhealthy. This makes debugging and performance tuning straightforward, even as your app grows.
Performance Optimization for Laravel on Kuberns
Kuberns applies Laravel’s recommended production optimizations automatically during deployment:
composer install —no-dev php artisan config:cache php artisan route:cache php artisan view:cache
For best performance, use Redis for:
- Session storage
- Cache
- Queue processing
This reduces database load and speeds up request handling, especially under traffic.
Why Deploying Laravel on Kuberns Is Simpler
Most Laravel deployments fail or become hard to maintain because the underlying environment drifts over time. Different PHP versions, missing extensions, mismatched queue settings, or forgotten cron entries are common causes of production issues. When every server is configured manually, it gets harder to keep staging and production consistent as the application grows.
Kuberns solves this by treating the environment as part of the deployment itself. Every deployment runs inside a preconfigured runtime where PHP, server settings, workers, scheduler, and environment variables are standardized. This means the application behaves the same in every environment, without surprises.
| Task | Typical Manual Setup | On Kuberns |
|---|---|---|
| PHP and extensions | Install and update manually | Preconfigured runtime provided |
| Web server configuration | Edit Nginx or Apache files | Already optimized for Laravel |
| Queue workers | Supervisor setup required | Worker enabled from dashboard |
| Scheduler (cron) | Add and maintain cron jobs | Scheduler toggle, runs automatically |
| SSL certificates | Install and renew with Certbot | One-click automatic SSL |
| Scaling | Requires DevOps knowledge | Auto or manual scaling built in |
| Debugging | SSH and log file digging | Live dashboard logs and alerts |
This is the same benefit highlighted in Deploy Nodejs on Netlify and why Kuberns is a smarter choice, where working with a consistent runtime reduces deployment complexity and prevents environment-level issues.
With Kuberns, you are not just deploying code. You are getting a consistent deployment pipeline that removes the need to configure or maintain infrastructure manually:
- Deploy directly from GitHub so every push can trigger a clean, repeatable build without uploading files or managing SSH access.
- Keep staging and production identical because Kuberns uses the same runtime environment for every deployment, avoiding the “works locally but not on server” problem.
- Avoid managing servers or system packages since PHP, web server configuration, queue processing, and SSL are already handled by the platform.
- Scale smoothly as workload grows by adjusting instance sizes or enabling auto scaling, without having to rebuild your deployment or introduce new tools.
In other words, your Laravel app remains focused on application logic, while Kuberns takes responsibility for everything that keeps it running fast, stable, and secure.
| Feature | Traditional VPS | Kuberns |
|---|---|---|
| Manual setup required | Yes | No |
| Queue workers setup | Manual | One click |
| SSL setup | Manual | One click |
| Scaling | Needs DevOps | Automatic or manual slider |
| Monitoring | Manual tools needed | Built in |
| Builds | Manual and variable | Automated & repeatable |
In short:
Laravel runs reliably because the environment is standardized, not improvised. You focus on your app. Kuberns handles the infrastructure that keeps it online.
Most teams choose Kuberns because it cuts down deploy time and prevents configuration drift between environments.
Common Deployment Problems (and How Kuberns Solves Them)
Most issues with Laravel deployments come from the environment, not the code. When every server is configured manually, small differences in versions, extensions, or service setup can cause unpredictable errors in production.
1. Environment Mismatch
Local, staging, and production often run different PHP versions or configuration settings. This leads to bugs that only appear after deploys.
How Kuberns solves it: Every deployment runs in the same standardized PHP environment, so your app behaves the same in all environments.
2. Queue Workers Stopping Unexpectedly
On a VPS, queue workers rely on Supervisor or system services. If the process dies, jobs stall silently.
How Kuberns solves it: Workers are run as managed processes that auto restart and can scale based on load.
3. Cron Jobs Not Running
Missing or misconfigured crontab entries can break scheduled tasks like email sending or cleanup jobs.
How Kuberns solves it: Enable the scheduler toggle and Kuberns runs php artisan schedule:run automatically without cron setup.
4. SSL Renewal Failures
Certbot and manual SSL management often lead to expired certificates if renewals fail.
How Kuberns solves it: Custom domains get automatic SSL renewal built in.
5. Debugging Requires SSH Access
Logs scattered across servers make troubleshooting slow.
How Kuberns solves it: Logs for web, workers, and scheduler are streamed in real time from the dashboard. No SSH required.
This predictable, environment-stable workflow is also reflected in other framework setups, as shown in the Node.js Deployment Tutorial in the Kuberns docs.
The principle is the same: stable runtime, minimal configuration, consistent deployments.
Final Thoughts
Laravel gives you a great development experience, but deployment is where many teams lose time. Configuring servers, managing PHP versions, setting up queue workers, scheduling tasks, updating SSL certificates, and scaling under traffic can quickly become operational overhead.
Kuberns removes that complexity. You connect your GitHub repository, set your environment variables, and deploy. The platform handles the runtime, workers, scheduler, scaling, logging, SSL, and monitoring behind the scenes. Your application behaves consistently across staging and production without needing DevOps expertise.
This makes Kuberns a strong fit for SaaS products, client projects, internal tools, agency workflows, and growing startups that want predictable deployments and lower infrastructure maintenance.
Start deploying Laravel the efficient way. Try Kuberns and experience how smooth your deployment workflow can be.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I deploy any Laravel version on Kuberns?
Yes. Kuberns supports Laravel apps running on modern PHP versions. The platform automatically selects the correct runtime and installs dependencies during deployment.
Do I need to write a Dockerfile to deploy Laravel?
No. Kuberns detects Laravel automatically and configures the runtime, web server, and build steps without requiring you to write a Dockerfile.
How do I add database credentials on Kuberns?
Go to the Environment section in the dashboard and enter your variables there. They are stored securely and injected into the application during runtime.
Does Kuberns support Redis for queues and caching?
Yes. You can connect your Redis instance or external provider. Once you add REDIS_HOST, REDIS_PORT, and credentials, Redis will work for cache, sessions, and queues.
Can I run Laravel queue workers on Kuberns?
Yes. You can enable a dedicated worker process from the dashboard and provide the worker command. The worker will auto restart if it stops.
How does Laravel scheduling work on Kuberns?
You do not need cron. Enable the scheduler in your service settings and Kuberns handles running php artisan schedule:run automatically at the correct interval.
Can I store user-uploaded files using Kuberns?
Yes. You can attach persistent storage or use S3-compatible storage by setting FILESYSTEM_DISK=s3 and adding your storage credentials to environment variables.
Does Kuberns provide free SSL for custom domains?
Yes. Add your domain in the dashboard, point DNS to Kuberns, and enable SSL with a single click. Certificates renew automatically.
How do I scale my Laravel app on Kuberns?
You can scale vertically by increasing resources, or horizontally by enabling auto scaling. Both options require no code changes or server configuration.
Is the deployment workflow similar for other frameworks?
Yes. Kuberns follows the same environment consistency approach across frameworks, as shown in the Node.js Deployment Tutorial, ensuring predictable deployments for mixed tech stacks.