Published
- 12 min read
How to Deploy a MERN App in 2025: A Complete Developer Guide

Deploying a MERN app is one of those things that looks simple when everything is running on localhost. Your React frontend works, your Express APIs respond, MongoDB connects without issues, and everything feels smooth. The real challenge starts when you move that setup to production and have to worry about builds, environment variables, routing, SSL, and database reliability.
In 2025, developers expect deployment to be simple. They want a workflow where they connect a GitHub repo, add environment variables, and ship a full stack app without touching servers or writing Docker files. This guide will walk you through how to deploy a MERN app in a clean and reliable way, and how Kuberns removes most of the DevOps work with automated full stack deployment.
If you want a broader view of how Kuberns handles full stack apps, you can also read What Is Kuberns? The Simplest Way to Build, Deploy, and Scale Full-Stack Apps and our practical guide How to Implement One-Click Automated Software Deployment.
What Exactly Is a MERN App
The MERN stack brings together MongoDB, Express, React, and Node to create a full stack JavaScript application. The main advantage of MERN is that you build both the frontend and backend using the same language, which makes development faster and easier to maintain.
React handles the UI, routing, and API calls, while the Express and Node side manages authentication, business logic, and the connection to MongoDB. This simple split works well during development, but it becomes more sensitive during deployment where every connection point must be configured correctly.
What matters most in a MERN app is how cleanly the two sides can talk to each other in production. Locally, everything runs on separate ports and works without much setup. In production, you have to ensure the React build is generated properly, the backend reads environment variables correctly, and the database connection is secure and reliable. Even small misconfigurations can lead to broken routes, CORS issues, or build failures.
The better your project is structured, the easier the deployment will be. A clear separation between client and server, well defined environment variables, and predictable API paths make the entire deployment flow much smoother, especially when you move to a cloud platform.
Preparing Your MERN App for Deployment
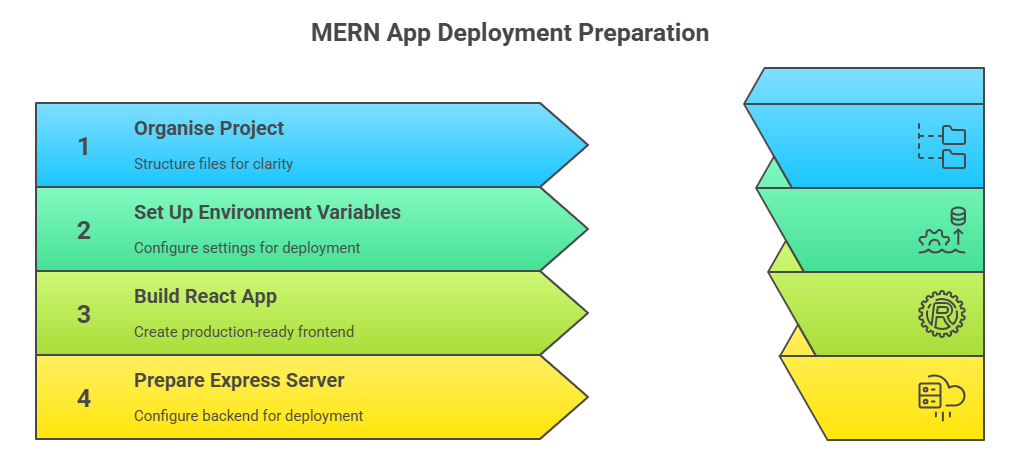 A smooth MERN deployment depends on having a clean structure and a few key preparations in place. These steps prevent most of the issues that appear only when you push your app to production.
A smooth MERN deployment depends on having a clean structure and a few key preparations in place. These steps prevent most of the issues that appear only when you push your app to production.
1. Organise your project
Keep your frontend and backend separate so the build process stays clear and predictable.
- client for React
- server for Express
- Each with its own package.json
This helps the deployment platform identify what needs to be built and how each part should run.
2. Set up environment variables
Your app should not depend on hardcoded values. Create a .env file during development for things like:
- MongoDB connection string
- JWT secret
- API base URL
- Port values
In production, these values will be added directly to your hosting platform for security.
3. Build the React app
Run the production build before deploying. This ensures your frontend is packaged into stable static assets that can be served by the backend or a hosting service.
A clean build here is important, because most frontend issues in production come from build failures or missing assets.
4. Prepare the Express server
Your backend should be ready for production by:
- Using a dynamic port
- Handling environment variables correctly
- Serving the React build if both run together
These small steps eliminate common deployment issues like port conflicts, broken routes, and CORS problems.
How to Deploy a MERN App: The Three Deployment Options
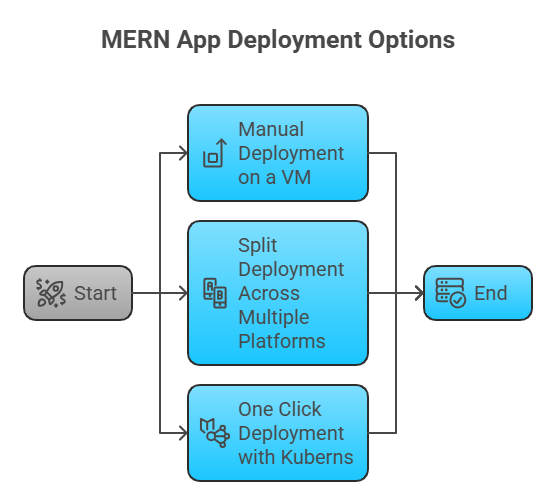 There are three common ways developers deploy MERN apps today, and each one offers a different balance between control, convenience, and maintenance. Understanding these options makes it easier to choose the workflow that fits your project.
There are three common ways developers deploy MERN apps today, and each one offers a different balance between control, convenience, and maintenance. Understanding these options makes it easier to choose the workflow that fits your project.
1. Manual Deployment on a VM
Manual deployment is the traditional way of hosting a MERN app. You create and manage everything yourself on a virtual machine, usually running Ubuntu. It gives you full control but also requires the most effort.
What this setup involves
- Creating an Ubuntu server
- Installing Node and npm
- Setting up nginx as a reverse proxy
- Running the backend with PM2 or a similar process manager
- Configuring SSL certificates
- Installing MongoDB locally or connecting to Atlas
- Handling updates, scaling, and backups on your own
Where it works well
This approach makes sense when you want complete control over your environment or when you are experimenting and want to understand how everything fits together under the hood.
Where it becomes difficult
As your application grows, this setup becomes harder to maintain. You must manage performance tuning, security patches, log rotation, scaling, service restarts, and deployment workflows. Adding zero downtime deploys or multiple environments usually requires more tooling and more manual work.
Manual deployment teaches you a lot, but for production apps it often becomes a source of overhead rather than stability.
2. Split Deployment Across Multiple Platforms
Many teams deploy their MERN app by separating the frontend, backend, and database across different services. It feels convenient in the beginning because each part sits on a platform designed specifically for it. A typical setup looks something like this:
- React hosted on a frontend platform
- Node and Express hosted on another provider
- MongoDB running on Atlas
This approach works for smaller projects, but the complexity grows quickly as your app becomes more serious. Each platform has its own way of handling deployments, logs, and environment variables, so updating something simple can take more time than expected. Backends on certain platforms may also face cold starts, which can slow down API responses. CORS issues are another common problem because the frontend and backend live on different domains.
The biggest challenge is maintenance. You are managing multiple dashboards, monitoring tools, and deployment settings, which makes debugging more complicated. As your application scales, this split model often becomes a source of friction instead of flexibility.
A more unified setup keeps both the frontend and backend in one place, which avoids these problems and makes deployments more predictable. We explain why this matters for full stack applications in our guide on One-Click Automated Deployment, where you can see how routing, builds, scaling, and SSL work together when everything runs under a single workflow.
3. One Click Deployment with Kuberns
 A one click workflow is the simplest way to deploy a MERN application. Kuberns removes the usual setup steps by detecting your frontend and backend automatically and building them in the correct order. You do not write Dockerfiles, configure nginx, or manage servers. The platform handles everything behind the scenes so the deployment experience stays consistent.
A one click workflow is the simplest way to deploy a MERN application. Kuberns removes the usual setup steps by detecting your frontend and backend automatically and building them in the correct order. You do not write Dockerfiles, configure nginx, or manage servers. The platform handles everything behind the scenes so the deployment experience stays consistent.
How the deployment flow works
- Connect your GitHub account
- Select your MERN repository
- Add your environment variables and click Deploy
Once you deploy, Kuberns builds your React app, sets up the Express backend, applies routing rules, provisions SSL, assigns ports, and runs your services on managed AWS infrastructure. Each update is deployed without downtime, which makes the workflow reliable for both solo developers and growing teams.
Why this approach matters
Keeping the entire MERN stack in one place removes the friction that usually appears when the frontend and backend are deployed separately. Logs, builds, environment variables, and scaling decisions stay unified. This leads to fewer surprises in production and a much simpler operational flow.
If you want to see how this fits into the overall platform, you can explore the product on Kuberns. Developers who want to try the deployment process directly can follow the quick start guide in the Kuberns Docs which walks through the setup step by step.
Setting Up MongoDB for Production
Most MERN applications use MongoDB Atlas in production because it is secure, managed, and removes the need to run your own database server. A correct Atlas setup is important, since many production deployment issues come from incorrect connection strings or IP restrictions.
A typical setup includes a few essential steps:
- Creating a cluster in Atlas
- Adding a dedicated database user
- Copying the connection string from the Dashboard
- Adding that connection string to your backend environment variables
The most important piece here is the connection string. Your Express server should always read this value from an environment variable rather than hardcoding it. This keeps your credentials secure and makes deployments predictable.
Where teams often get stuck
MongoDB Atlas requires you to whitelist IP addresses so only approved servers can access your database. When you deploy on traditional platforms, the app may run across changing or unknown IPs, which causes random database connection failures. Developers usually have to temporarily allow all IP addresses or constantly update their Atlas configuration, both of which become frustrating in production.
How Kuberns simplifies this
Kuberns removes the need for manual IP whitelisting. When your MERN application connects to MongoDB, the platform proxies requests through a stable internal network layer. This means:
- No IP changes to track
- No manual updates in Atlas
- No random connection errors after redeploys
- The database connection stays stable across scaling events
You only paste your MONGO_URI into the environment variables inside the Kuberns dashboard and it works immediately. This makes database configuration one of the easiest parts of deploying a MERN app on Kuberns, especially compared to platforms where IP management becomes an ongoing headache.
With MongoDB configured correctly and Kuberns handling network access automatically, you eliminate one of the biggest friction points in MERN deployments and ensure your backend can connect reliably in production.
Deploying the MERN Frontend and Backend
The deployment process depends on whether your frontend and backend live together or on separate services. Both approaches work, but they create very different levels of complexity once you move past development and into real production environments.
Deploying Separately
Some teams host the React frontend and the Node backend on different platforms. The workflow usually looks like this:
- Uploading the React production build to a frontend hosting service
- Deploying the backend on another provider
- Updating REACT_APP_API_URL to point to the backend URL
- Rebuilding the frontend after updating the API URL
- Setting and maintaining environment variables across two platforms
This setup works, but it becomes harder to maintain over time. Each platform handles builds, variables, logs, and routing differently. Debugging also becomes more difficult because you now have to switch between multiple dashboards to find where an error actually occurred.
This approach is fine for small projects, but for production you start to feel the friction as the app grows.
Deploying with Kuberns in One Go
Kuberns gives you a single, consistent workflow for deploying both the frontend and backend of your MERN app. You still deploy both parts, but you do it from one place, which removes the usual back and forth between multiple platforms. Once your GitHub repo is connected, Kuberns automatically identifies your React and Express folders and runs the correct build steps for each. This keeps the deployment clean and avoids the common routing or build issues that appear on manual setups.
The important advantage here is that you do not manage any infrastructure. Kuberns handles routing, port assignments, SSL, and runtime configuration in the background. It also keeps your logs, environment variables, and deployments together in a single dashboard, so you always know where to look when you update or debug your application.
By keeping everything unified, every deployment behaves predictably and your services stay connected without downtime. This is what makes deploying a MERN application on Kuberns much simpler than juggling separate hosting services or maintaining your own servers.
Mapping Your Domain and SSL Certificates
A production MERN app needs a custom domain and a secure HTTPS connection. When you deploy manually, this usually means configuring nginx, installing Certbot, renewing certificates, and managing redirects and firewall rules. It works, but it takes effort to keep everything updated and secure.
With Kuberns, this entire process is simplified. You add your domain in the dashboard, and the platform automatically issues and renews SSL certificates, applies the routing, and enables HTTPS without any extra configuration. This removes a major source of deployment complexity and keeps your app secure from day one with no manual setup required.
Production Checklist for a MERN App
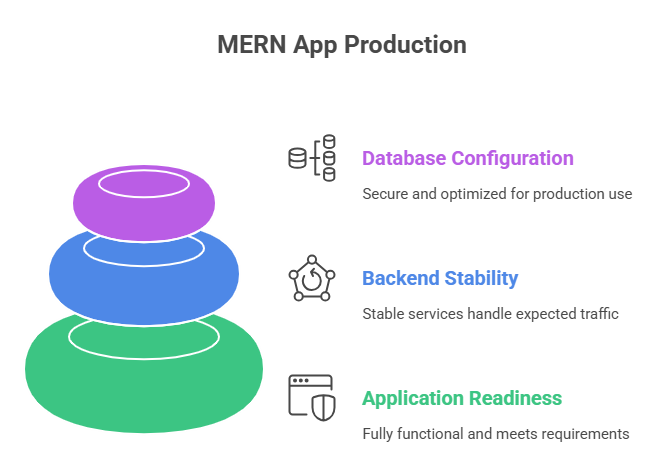 A final production check ensures your MERN app behaves the same way in the cloud as it does on your local machine. Most deployment issues come from small misconfigurations, so validating these areas before going live helps avoid downtime or unexpected errors.
A final production check ensures your MERN app behaves the same way in the cloud as it does on your local machine. Most deployment issues come from small misconfigurations, so validating these areas before going live helps avoid downtime or unexpected errors.
1. Application readiness
Your React build should load cleanly without broken links, missing assets, or routing issues. Ensure that the API requests from the frontend reach the backend correctly and that authentication flows like login and signup work as expected. If your app uses tokens or sessions, verify that they persist across page reloads and expire correctly.
2. Backend stability
Confirm that environment variables are properly configured and that the backend is reading them in production. This is where many database and secret-related errors occur. CORS should allow the required domains, and rate limiting or basic security checks should be in place to protect your API endpoints. Clean logs and clear error messages help you track issues quickly once users start interacting with the app.
3. Database configuration
Your MongoDB instance should connect reliably from your hosting platform. Make sure the connection string is correct, indexes are created for any frequently queried fields, and test collections left over from development are removed. A clean and indexed database not only prevents errors but also improves performance under load.
Completing this checklist helps eliminate most of the common issues that appear after deployment and ensures your MERN app is stable, secure, and ready to handle real users.
Final Thoughts
Deploying a MERN app does not have to be a complex, multi-step process. The framework itself is straightforward, and your deployment workflow should feel the same way. When your frontend, backend, and database are prepared correctly, the last mile of bringing your application online becomes much simpler.
Kuberns removes the need for server setup, Dockerfiles, reverse proxies, and manual SSL work. You connect your GitHub repo, add your environment variables, and deploy both parts of your MERN app from one place. The platform handles the infrastructure so your focus stays on building features, not managing configurations.
If you are ready to deploy your MERN app with a workflow designed for full stack development, you can start in minutes with the Kuberns Quick Start Guide or explore the platform directly at kuberns

Frequently Asked Questions
How do I deploy a MERN app with one click?
You can deploy a MERN app on Kuberns by connecting your GitHub repo and adding your environment variables. The platform handles builds, SSL, routing, and scaling.
Is MongoDB Atlas required for MERN apps?
Not required but recommended. It offers automated backups, security, and performance without managing server installations.
Should I host frontend and backend separately?
You can, but hosting everything together on a single platform reduces CORS issues and deployment friction.
Does a MERN app need Docker?
Only if you are deploying manually. But platforms like Kuberns generate containers automatically from your code.