Published
- 14 min read
FastAPI Deployment Guide 2025: How to Deploy FastAPI Easily

FastAPI has become one of the most popular frameworks for building high-performance APIs in Python because it is lightweight, async friendly and designed around modern development patterns.
It gives you automatic OpenAPI documentation, type validated request handling through Pydantic and a clean, intuitive development experience.
The real challenge appears when you move from local development to production. Deploying a FastAPI application is not the same as deploying a simple Python script or a Django project.
You need an ASGI server, a stable process manager, SSL, environment variable management and the ability to scale without breaking your API when traffic increases.
If these pieces are not configured properly, you may run into problems such as slow responses, worker crashes, inconsistent performance, missing environment values and proxy related issues that only show up under real-world conditions.
This guide explains everything you need to deploy FastAPI correctly in 2025. You will learn:
- How FastAPI behaves in production
- Deployment methods and when to choose each
- A clear step by step workflow to deploy FastAPI on Kuberns
- Best practices for performance, scaling and secrets
- When managed hosting is a better choice than manual servers
If you want a simple background on Python deployment before starting, you can read this introductory guide on deploying Python applications with AI support published on the Kuberns blog.
The article is available here and provides a helpful foundation for beginners: how to deploy python app with ai
Why FastAPI Needs a Proper Production Setup?
FastAPI is built on ASGI, which means it is designed for high speed, async communication and efficient concurrency handling. These benefits only appear in production when the environment is configured correctly.
Unlike older Python frameworks that rely on WSGI, FastAPI requires an ASGI server such as Uvicorn or Hypercorn and a process manager that can coordinate multiple async workers.
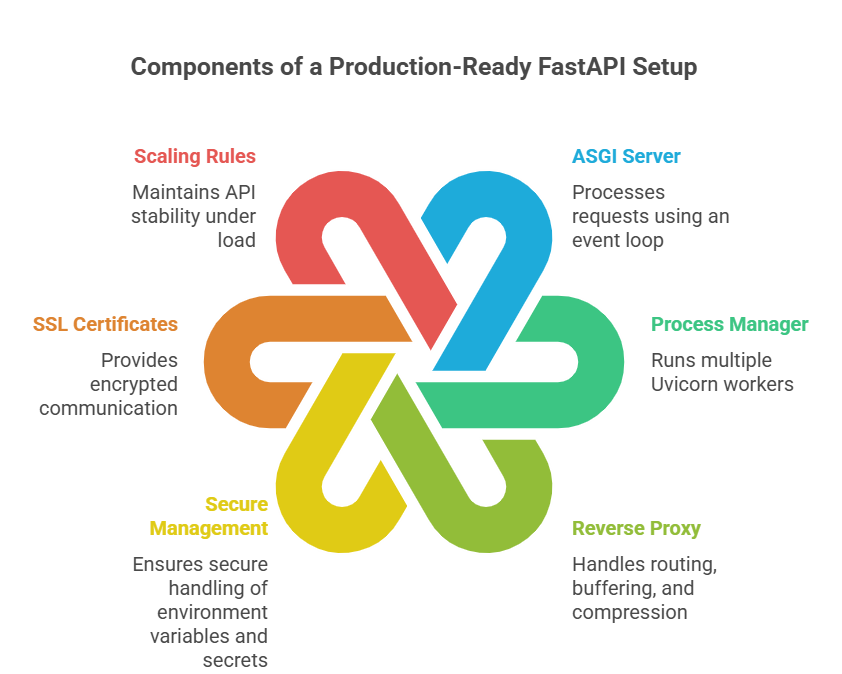 A complete production-ready setup usually includes:
A complete production-ready setup usually includes:
- ASGI server to process requests using an event loop
- Process manager like Gunicorn to run multiple Uvicorn workers
- Reverse proxy to handle routing, buffering and compression
- Secure management of environment variables and secrets
- SSL certificates for encrypted communication
- Scaling rules or resource limits to keep the API stable under load
Each part plays a role in API reliability. For example, running a single Uvicorn worker without a process manager can cause requests to slow down or queue up.
Missing a reverse proxy may lead to issues with large payloads or socket timeouts. Poor environment variable handling can break deployments when API keys or database credentials change.
Handling all this manually on a VPS is possible, but it becomes difficult as soon as your API grows, serves real users or becomes part of a microservice architecture.
This is one reason many developers working with FastAPI prefer a managed platform.
You can see how modern deployment environments handle these components in the Kuberns guide on deploying Node.js applications, which explains automated builds, logs and scaling in a practical way.
A stable and properly configured production setup ensures your FastAPI API remains consistent, fast and reliable even during sudden traffic spikes.
Deployment Options For FastAPI in 2025
FastAPI can be deployed in multiple ways depending on your expertise, the size of your project and how much infrastructure you want to manage.
Each option has its benefits, limitations and maintenance overhead, so choosing the right one affects your API’s performance and long-term reliability.
1. Deploy on a Virtual Machine
Platforms like EC2, DigitalOcean or Linode give you complete control over your environment. You manage everything from the operating system to the network configuration. A typical manual setup includes:
- Provisioning and securing the server
- Installing and configuring Uvicorn or Gunicorn
- Setting up Systemd services for reliable worker restarts
- Configuring a reverse proxy like Nginx for performance and routing
- Handling OS level updates and security patches
- Managing scaling limits and instance upgrades
- Monitoring system load, logs and traffic behaviour
This method offers maximum flexibility but demands deep DevOps knowledge. It works for teams who need full customization, but it slows down indie developers and fast moving startups who prefer to focus on shipping features.
2. Deploy using Docker or Kubernetes
 Containerizing your FastAPI app gives you a consistent environment across development, staging and production. It also makes deployments repeatable. However, it introduces extra responsibilities like:
Containerizing your FastAPI app gives you a consistent environment across development, staging and production. It also makes deployments repeatable. However, it introduces extra responsibilities like:
- Writing and optimizing a Dockerfile for smaller image sizes
- Using multi-stage builds to reduce dependency bloat
- Managing container registries and image pushes
- Creating Kubernetes manifests for deployment, service and ingress
- Handling load balancing, secrets and service discovery
- Setting up autoscaling rules for CPU or request based scaling
This is a strong choice for large teams, distributed systems or enterprise deployments that require fine grained control. It is powerful but significantly more complex than other options.
3. Deploy on PaaS Platforms such as Kuberns
 For most developers in 2025, a PaaS platform removes unnecessary operational complexity. Instead of maintaining servers, you connect your repository and let the platform automate the infrastructure layer. With Kuberns, you get:
For most developers in 2025, a PaaS platform removes unnecessary operational complexity. Instead of maintaining servers, you connect your repository and let the platform automate the infrastructure layer. With Kuberns, you get:
- Automatic build and containerization
- Zero configuration scaling
- Free SSL
- Centralized logs and monitoring
- Health checks and auto restarts
- Rollback support for safe releases
PaaS is ideal for teams who want reliable deployment without writing Dockerfiles or configuring proxies.
You can see how this automated pattern works in one of the Kuberns Python compatible guides, such as the tutorial on deploying a Next.js application, which follows the same deployment pipeline used for FastAPI services.
How To Deploy a FastAPI App on Kuberns
Deploying a FastAPI application on Kuberns is fast because the platform takes care of the entire backend setup for you. It builds the container, installs dependencies, prepares the environment, runs Uvicorn workers and configures HTTPS without any manual steps.
Instead of handling servers or writing Dockerfiles, you work directly from your GitHub repository and let the platform manage the rest.
Step 1: Push Your FastAPI Project to GitHub
 Your repository should contain your application file like main.py or app.py and a requirements.txt file. This gives Kuberns enough information to detect your Python environment. If you prefer full control, you can still include a Dockerfile, but it is not required.
Your repository should contain your application file like main.py or app.py and a requirements.txt file. This gives Kuberns enough information to detect your Python environment. If you prefer full control, you can still include a Dockerfile, but it is not required.
Step 2: Connect Your Repository to Kuberns
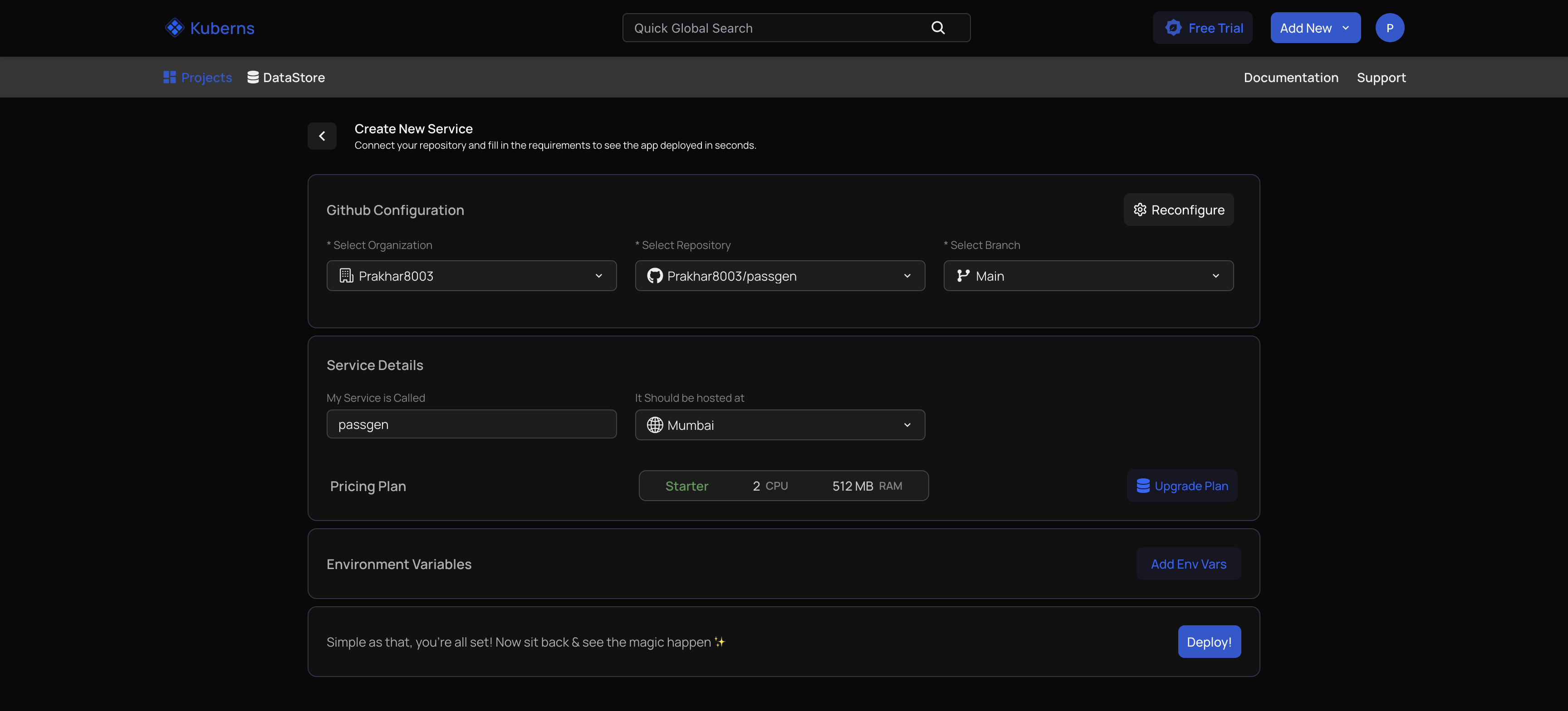 After clicking New Project, connect GitHub and choose your FastAPI repo. Kuberns will automatically detect that it is a Python project, prepare the build environment and pull the latest code. This removes the usual setup steps that developers configure manually on VPS or Docker-based deployments.
After clicking New Project, connect GitHub and choose your FastAPI repo. Kuberns will automatically detect that it is a Python project, prepare the build environment and pull the latest code. This removes the usual setup steps that developers configure manually on VPS or Docker-based deployments.
Step 3: Configure Build and Start Commands
Most projects are detected automatically, but you can specify commands if needed. The build typically installs your dependencies, and the start command launches Uvicorn. This ensures the application runs on an ASGI server that supports concurrency and high performance.
Step 4: Add Environment Variables
 Production APIs depend on secure configuration, so this is where you add values like database URLs, API keys or JWT secrets. Kuberns stores them in encrypted form and injects them during runtime, allowing you to keep sensitive information out of your code.
Production APIs depend on secure configuration, so this is where you add values like database URLs, API keys or JWT secrets. Kuberns stores them in encrypted form and injects them during runtime, allowing you to keep sensitive information out of your code.
Step 5: Deploy
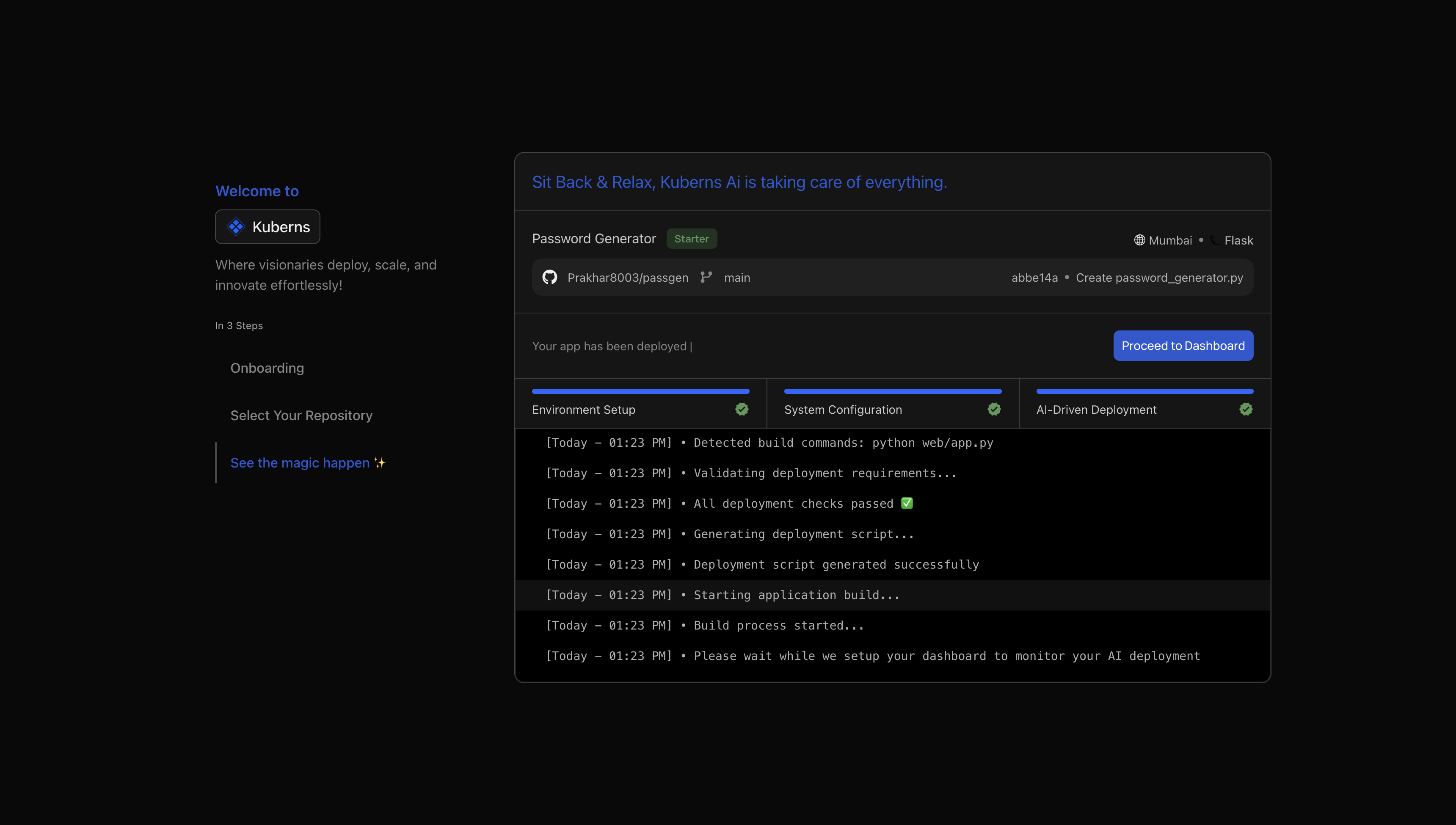 Once you click Deploy, the platform handles the complete workflow: installing dependencies, generating a container image, provisioning the environment, running Uvicorn workers, adding SSL and preparing a live URL.
Once you click Deploy, the platform handles the complete workflow: installing dependencies, generating a container image, provisioning the environment, running Uvicorn workers, adding SSL and preparing a live URL.
Logs and health checks are enabled automatically so you can observe your API from the dashboard. Within seconds, the application becomes fully accessible and ready to scale based on traffic.
If you want to understand how Kuberns manages build pipelines and runtime environments for Python projects in general, the guide on how to deploy a Python app with AI explains the underlying workflow in a simple way and follows the same deployment pattern FastAPI uses.
Best Practices for FastAPI Deployment
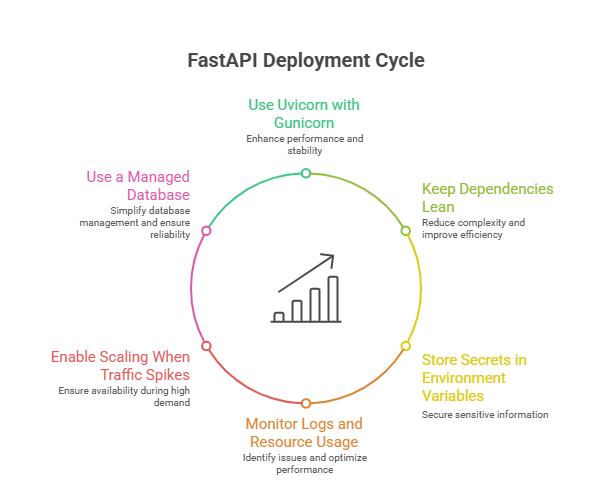 FastAPI performs best when the production environment is set up with the right workers, scaling configuration and dependency structure.
FastAPI performs best when the production environment is set up with the right workers, scaling configuration and dependency structure.
These practices help your API remain fast, stable and consistent as traffic increases.
Use Uvicorn with Gunicorn
Running Uvicorn under Gunicorn improves concurrency and ensures the server can handle multiple simultaneous requests smoothly.
Keep Dependencies Lean
A small and clean requirements.txt reduces build time and creates lighter containers. Removing unused libraries keeps deployments efficient.
Store Secrets in Environment Variables
Use environment variables for database URLs, API keys and other sensitive values. This improves security and keeps your codebase clean.
Monitor Logs and Resource Usage
Keeping an eye on CPU, memory, and logs helps you detect slow endpoints, heavy background tasks or early signs of performance issues.
Enable Scaling When Traffic Spikes
If your API receives unpredictable traffic, scaling workers or instance size ensures stable response times during peak usage.
Use a Managed Database
Hosted PostgreSQL or managed services like Neon and Supabase offer better reliability and reduce maintenance work.
If you want to see how Kuberns handles runtime setup, build steps and production environments across different languages, the guide on how to deploy a Node.js app uses the same deployment flow your FastAPI service will follow.
When To Choose Kuberns for FastAPI Deployment
FastAPI applications start small but can scale quickly when used for real APIs, dashboards, internal tools or background processing.
When your project begins handling real users, managing infrastructure manually becomes harder.
A platform like Kuberns makes this easier by handling the operational side of deployment so you can focus on your code.
When you want infrastructure handled for you
Kuberns automatically builds and containerises your FastAPI app, sets up Uvicorn workers, provisions a production environment and manages SSL. This removes the need to configure servers, write Dockerfiles or deal with system dependencies.
When you expect your API to grow
FastAPI performs very well under load, but only when scaling is managed properly. Kuberns supports automatic scaling, controlled resource limits and consistent environments so your API remains stable during traffic spikes.
When you want built-in monitoring and logs
Instead of setting up log forwarding or third-party tools, Kuberns gives you real-time logs, health checks and metrics directly in the dashboard. This helps you catch performance issues early.
When you want fast deploys without DevOps work
With one click, redeploys, version control-based workflow and secure environment variable management, Kuberns simplifies the entire process. This is especially useful for teams shipping updates frequently.
Conclusion
FastAPI makes API development fast and efficient, but the real performance advantage appears only when it is deployed in a stable, production-ready environment. Choosing the right deployment approach affects everything from response time to scalability, error handling and long-term reliability.
Manual setups work for experimentation, but as your API grows or begins serving real users, infrastructure management becomes a time consuming burden.
Kuberns solves this problem by giving you a deployment workflow that handles the entire backend setup automatically.
You do not write Dockerfiles, configure Nginx, manage Uvicorn workers or set up SSL. The platform builds your app, provisions the runtime, enables scaling, provides logs and gives you a live URL within seconds.
It is built for developers who want a simple, reliable way to deploy modern Python applications without the overhead of DevOps.
If you want to deploy your FastAPI application with a workflow that is fast, stable and designed for real production use, you can start using Kuberns today. Explore Kuberns and deploy your FastAPI app in minutes
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I deploy FastAPI without using Docker?
Yes. You can deploy FastAPI directly on platforms like Kuberns or on a virtual machine using Uvicorn and Gunicorn. Docker is helpful but not required.
2. What is the best ASGI server for FastAPI in production?
Uvicorn is the most common ASGI server for FastAPI. In production, it is usually paired with Gunicorn to run multiple workers for better performance.
3. How many workers should I run for a FastAPI app?
A practical starting point is one worker for each CPU core. You can adjust based on traffic, memory usage and response times.
4. Do I need Nginx to deploy a FastAPI application?
You do not always need Nginx. Managed platforms handle reverse proxies for you. If you deploy on a VPS, Nginx helps with routing, buffering and SSL.
5. How do I manage environment variables in FastAPI?
Store them outside the code using environment variables. Platforms like Kuberns provide a secure interface to add and update these values during deployment.
6. Does FastAPI scale well under high traffic?
Yes. FastAPI handles concurrency efficiently, but scaling depends on workers, server resources and your hosting setup. Managed platforms make this much easier.
7. Can I use a database like PostgreSQL or MongoDB with FastAPI?
Yes. FastAPI works with PostgreSQL, MongoDB and other databases using ORM libraries or direct drivers. Use environment variables to store connection URLs.
8. How can I monitor FastAPI performance in production?
Monitor logs, CPU, memory and request patterns. Managed platforms provide built-in log streams and metrics that help detect bottlenecks early.
9. Does FastAPI work with background tasks or scheduled jobs?
Yes. FastAPI supports background tasks, and you can run them on separate workers or services depending on your workload.
10. What is the simplest way to deploy a FastAPI app today?
Using a managed deployment platform is the fastest approach because you avoid server setup, SSL configuration and manual scaling. It lets you deploy in minutes.